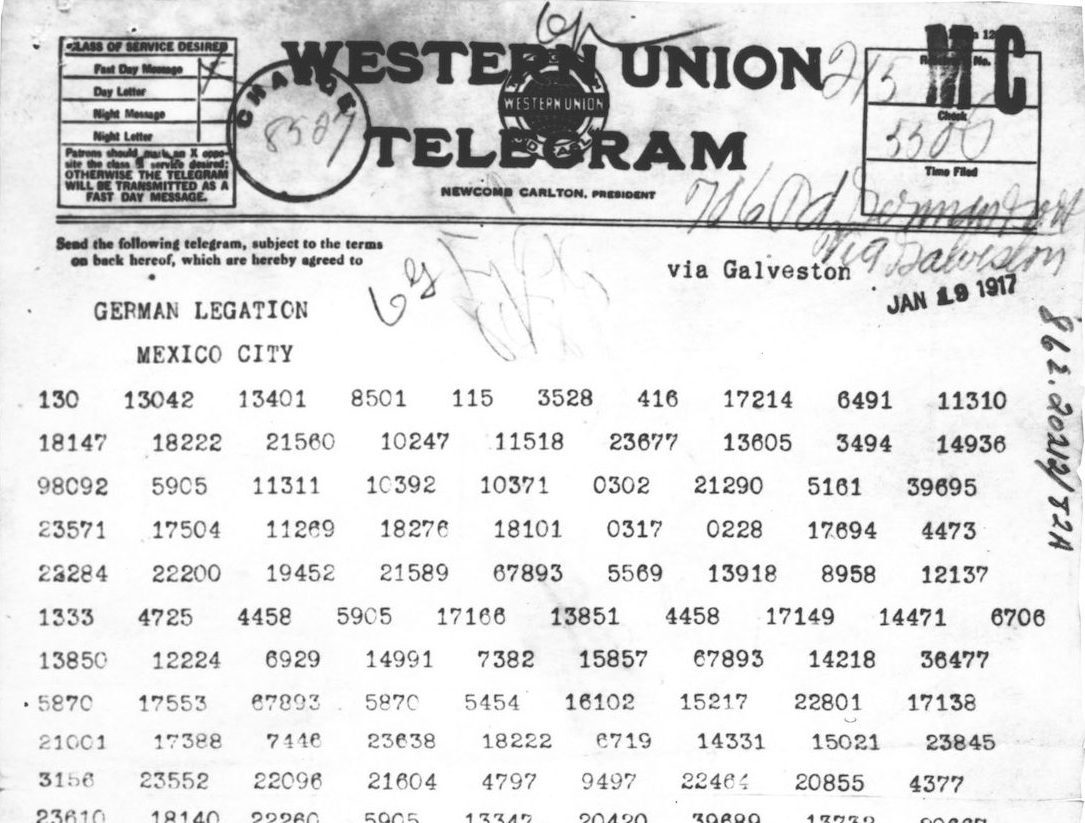
The Zimmermann Telegram was a pivotal moment in history that changed the course of World War I and ushered the United States into the conflict. Sent by German Foreign Minister Arthur Zimmermann to Mexico in January 1917, this secret diplomatic communication promised Mexico the territories of Texas, New Mexico, and Arizona if they joined forces with Germany against the United States. This bold move not only heightened tensions but also sparked outrage among Americans, contributing significantly to their decision to enter the war. Let’s dive deeper into the details surrounding this infamous telegram and its consequences.
The Context of World War I

To fully grasp the implications of the Zimmermann Telegram, we need to understand the global landscape of the time. World War I, which began in 1914, involved major world powers divided into two main alliances: the Allies and the Central Powers. Here’s a brief overview:
| Allies | Central Powers |
|---|---|
| United Kingdom | Germany |
| France | Austro-Hungarian Empire |
| Russia | Ottoman Empire |
| Italy (joined Allies in 1915) | Bulgaria |
Initially, the United States maintained a position of neutrality, largely due to its diverse population and economic interests. However, several factors were slowly pushing the U.S. toward involvement:
- Unrestricted Submarine Warfare: Germany's policy of sinking ships, including civilian ones, escalated tensions.
- Economic Ties: The U.S. had strong financial interests in supporting the Allies, particularly through trade and loans.
- Propaganda: British propaganda painted Germany in a negative light, shaping public perceptions.
Against this backdrop, the Zimmermann Telegram emerged as a direct threat to national security, igniting public outrage and marking a turning point in the U.S. stance on the war.
Read This: How to Make GIFs on Telegram: Creating Animated GIFs in Chats
What Was the Zimmermann Telegram?
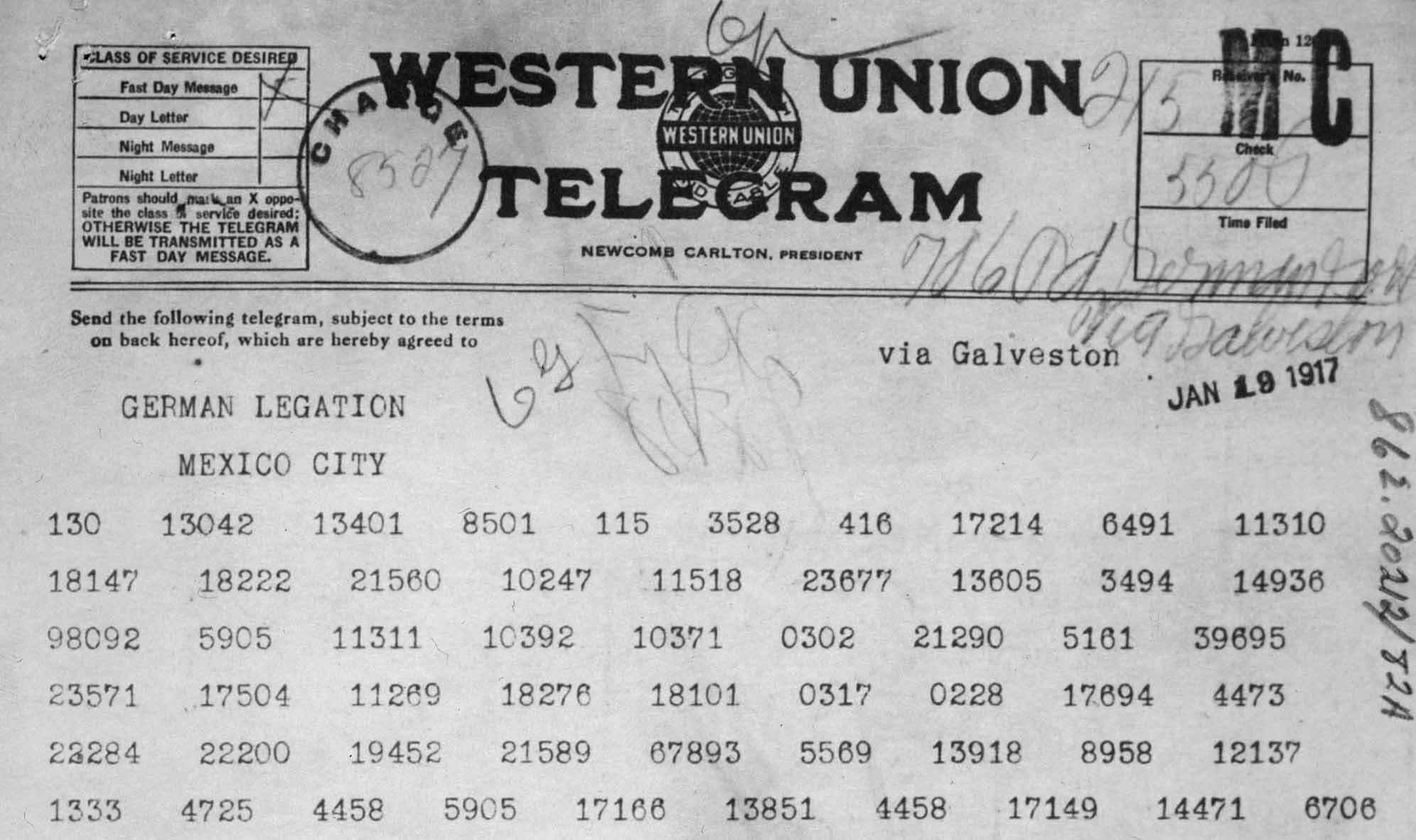
The Zimmermann Telegram was a secret diplomatic communication sent by the German Empire on January 16, 1917, during World War I. This message was addressed to the German ambassador in Mexico, Heinrich von Eckardt, and was intended to be delivered to the Mexican government. It's widely regarded as one of the pivotal moments that led the United States to enter the war. But what was actually in this telegram?
In the telegram, German Foreign Minister Arthur Zimmermann proposed a military alliance between Germany and Mexico in the event that the United States entered the war against Germany. To sweeten the deal, Zimmermann promised Mexico the territories of Texas, New Mexico, and Arizona as a reward for their cooperation. The message read:
- Germany would support Mexico in reclaiming lost territories.
- Germany would do its utmost to provoke conflict between the United States and Mexico.
This message was seen as a direct threat to U.S. national security and sovereignty. When British intelligence intercepted and decrypted the telegram, they swiftly shared it with the United States, introducing a mix of outrage and disbelief among American officials and the public. This exposure not only escalated anti-German sentiment in the U.S. but also solidified the notion that entering the war was a necessity. In a sense, it was like poking a sleeping bear.
To sum it up, the Zimmermann Telegram wasn't just a diplomatic communication; it was a calculated gamble by Germany that ultimately backfired spectacularly, altering the course of history.
Read This: How to Add Someone as an Admin in Telegram
Key Players Involved: Germany, Mexico, and the United States

The Zimmermann Telegram was not merely a one-way street involving Germany; it had key players whose motivations and actions were critical in shaping the outcome of World War I. Let's break down the three main players: Germany, Mexico, and the United States.
Germany
Germany, facing a two-front war with opponents like France and Britain, was in a desperate situation by 1917. Arthur Zimmermann, the German Foreign Minister, sought to distract the U.S. and create a conflict by pulling Mexico into the fray. His belief was that if Mexico was busy fighting the United States, it wouldn't be able to support the Allies effectively. Germany had a lot riding on this gambit, and the Zimmermann Telegram was their strategy to alter the war's course.
Mexico
On the Mexican side, the country was in the midst of its own revolution and was not necessarily looking to engage in another conflict. However, the proposition of reclaiming lost territories in Texas, New Mexico, and Arizona was a tantalizing offer. Mexican President Venustiano Carranza had to weigh his options, knowing that accepting such an alliance could lead to further turmoil in his already unstable nation. This made Mexico a somewhat reluctant but pivotal player in the drama that unfolded.
The United States
For the United States, the Zimmermann Telegram served as a jaw-dropping revelation. Up until that point, many American citizens were still holding onto the hope of staying neutral in the war. The telegram changed this sentiment quickly, igniting public outrage. President Woodrow Wilson, who had campaigned on the promise of keeping the U.S. out of the conflict, faced mounting pressure to act decisively. Ultimately, the telegram played a significant role in pushing the U.S. over the edge, leading to its official entry into World War I in April 1917.
So, when it comes to the Zimmermann Telegram, it was a tangled web of intrigue, desperation, and misguided strategies among Germany, Mexico, and the United States. Their actions combined to create a turning point in history, altering the landscape of global politics forever.
Read This: How to Download All Videos from Telegram at Once
The Contents of the Telegram and Its Implications
The Zimmermann Telegram, sent in January 1917 by German Foreign Minister Arthur Zimmermann to the German ambassador in Mexico, was a pivotal moment in World War I and in U.S. history. The message was intriguing yet alarming; it proposed a military alliance between Germany and Mexico in the event that the United States entered the war. In essence, Germany offered Mexico financial support and the prospect of regaining lost territories: Texas, New Mexico, and Arizona. This proposition wasn't just a simple diplomatic overture—it was a bold strategy to distract the U.S. while also increasing tensions on its southern border.
The implications of the telegram were profound. Firstly, it revealed Germany’s desperation to keep the U.S. occupied elsewhere, highlighting how critical America’s involvement was to the conflict. This audacious plan rattled the American public and government, as it suggested that Germany was willing to actively provoke hostility between Mexico and the U.S.
Moreover, this communication underscored a larger trend: Germany’s unrestricted submarine warfare meant that American lives and commerce were already threatened. Together, these elements stirred a sense of impending danger, awakening American nationalism and solidarity against a common foe.
In summary, the Zimmermann Telegram not only contained a startling proposal that shocked U.S. policymakers, but it also served as a catalyst that changed public opinion, positioning Americans to rally for involvement in World War I. Its contents were not just words; they embodied a shift towards a more aggressive U.S. foreign policy.
Read This: How to Create a Free Virtual Number for Telegram Registration
Immediate Reactions in the United States
The revelation of the Zimmermann Telegram sparked widespread outrage and alarm across the United States. As the telegram made its way into the hands of government officials and the press, the reaction was swift and intense. Americans were appalled at the mere idea of Germany attempting to incite a war with its neighbor to the south. Let’s take a closer look at some of the immediate reactions:
- Government Officials: Key leaders, including President Woodrow Wilson, were deeply concerned about the implications of this diplomatic attempt. Wilson had initially favored neutrality, but the telegram shifted his stance significantly.
- The Press: Newspapers exploded with sensational headlines about the telegram. Wildly publicized, the message galvanized public sentiment against Germany, fueling pro-war rhetoric.
- Public Sentiment: As news spread, everyday Americans found themselves outraged. Many began to see Germany not just as a distant foreign adversary but as a direct threat to their homeland.
The U.S. Congress quickly became a battleground for opinions on entering the war. Debates centered around patriotism and defending the nation against foreign intervention. Public rallies and campaigns sprang up, calling for solidarity and a decisive response.
Ultimately, the Zimmermann Telegram acted as a turning point that transformed American neutrality into active engagement. Less than three months after its unveiling, the United States would declare war on Germany, stepping firmly into the global conflict of World War I.
Read This: How to Add Your Telegram Username to Your Profile
The Role of Propaganda and Media
The Zimmermann Telegram was more than just a secret telegram; it became a key piece of propaganda that swayed public sentiment in America during World War I. As soon as the telegram was decrypted and made public, the U.S. government and various media outlets seized the opportunity to amplify its significance. The communication revealed that Germany was proposing a military alliance with Mexico, encouraging them to attack the United States. This revelation didn’t just make for intriguing news; it became a powerful tool in shaping public opinion.
Media outlets at the time—from newspapers to pamphlets—played a crucial role in disseminating the contents of the telegram. The sensational nature of the story guaranteed front-page coverage, sparking outrage among Americans. Here are a few ways propaganda and media influenced the response:
- Exaggeration of Threat: News organizations simplified the complexities of international politics, painting Germany as a clear threat to American sovereignty.
- Emotional Appeal: Journalists and editors invoked patriotic sentiments and feelings of fear, urging citizens to support the war effort.
- Call to Action: Media campaigns encouraged enlistment in the military, contributing to the growing tide of American involvement in World War I.
In essence, the media didn't just report the news; it took on an activist role that helped mobilize the nation towards war. Public figures also utilized the telegram in speeches, framing it as part of a larger narrative of American honor and moral duty to protect the nation. This concerted effort meant that the Zimmermann Telegram became far more than just a diplomatic blunder; it morphed into a rallying cry for American involvement in the war.
Read This: How to Search for Someone on Telegram: Finding Users and Groups Easily
Impact on American Public Opinion
The release of the Zimmermann Telegram had a monumental impact on American public opinion, transforming what was once a largely isolationist sentiment into a fervent desire to engage in World War I. Prior to the telegram's unveiling, many Americans believed in neutrality, largely influenced by sentiments from President Woodrow Wilson himself, who campaigned on keeping the nation out of European conflicts. However, the telegram shifted the landscape dramatically.
Here are some key points that illustrate the impact:
- Heightened Anti-German Sentiment: The telegram stoked feelings of mistrust and anger towards Germany, leading to a significant increase in anti-German propaganda.
- Shift in Public Sentiment: Polls taken after the telegram's release revealed a growing support for military action, with many Americans believing that the nation had to act to protect itself.
- Unity in National Identity: The perceived threat from Germany encouraged a sense of unity among Americans, galvanizing diverse groups—immigrants, women, and even pacifists—around the war effort.
Moreover, the telegram served as a catalyst for other events that fueled war fervor. It fueled the "Four Minute Men," a group of volunteers who gave short patriotic speeches in theaters across the country, and it inspired countless war posters urging enlistment and support for the troops. Ultimately, it played a crucial role in shaping American identity and led to a decisive moment where the U.S. shifted from isolationism to being an active participant in global conflict.
Read This: Telegram Group Link Viral Video
The U.S. Decision to Enter World War I
The Zimmermann Telegram, sent in January 1917 by German Foreign Minister Arthur Zimmermann to Mexico, served as a catalyst that propelled the United States into World War I. Until then, the U.S. had maintained a stance of neutrality, despite the ongoing conflict in Europe. The telegram proposed a military alliance between Germany and Mexico against the United States, promising the return of Texas, New Mexico, and Arizona to Mexico if Germany won the war.
When the British intercepted the telegram and shared it with the U.S. government, the implications were profound. Many Americans were already uneasy about Germany's unrestricted submarine warfare, which threatened American merchant ships and lives. The revelation of the Zimmermann Telegram pushed public opinion further against Germany, creating a swell of support for intervention. Key points leading to the U.S. decision included:
- Public Outrage: The idea of a potential attack on U.S. soil incited anger and fear among Americans.
- Allied Support: The U.S. had strong ties with Britain and France, and many felt a moral obligation to assist them.
- Economic Interests: American banks and businesses had financial stakes in an Allied victory.
On April 6, 1917, feeling the pressure from both the public and influential leaders, the U.S. Congress declared war on Germany. This marked a significant turning point in World War I, shifting the balance of power and leading to the eventual defeat of the Central Powers.
Read This: How to Add Another Account on Telegram for Android: A Step-by-Step Guide
Long-term Consequences of the Telegram
The implications of the Zimmermann Telegram extended far beyond the immediate entry of the United States into World War I. Its impact can still be felt in various ways today, shaping political alliances, national identities, and international relations. Here are some of the key long-term consequences:
- U.S.-Mexico Relations: The telegram heightened tensions between the U.S. and Mexico. Though war between the two nations was averted, the historical resentment persisted, affecting diplomatic relations for decades.
- Shift in U.S. Foreign Policy: The entry into WWI marked the beginning of a more interventionist U.S. foreign policy, abandoning its previous approach of isolationism.
- Strengthened Alliances: The U.S. solidified its role on the world stage, establishing strong bonds with Allied nations that would influence future conflicts, including World War II.
- Domestic Impact: The war effort led to social changes within the U.S., including the acceleration of women's suffrage, as women played vital roles in the workforce and military.
In retrospect, the Zimmermann Telegram was not just a diplomatic blunder for Germany but a pivotal moment that reshaped global dynamics and set precedents affecting international relations into the modern era.
Read This: How to Add Someone on Telegram Using Their Username: A Step-by-Step Guide
Why Did the Zimmermann Telegram Upset the United States?
The Zimmermann Telegram, sent in January 1917 by Germany's Foreign Minister Arthur Zimmermann to Mexico, marked a pivotal moment in World War I and significantly shifted U.S. public opinion against Germany. This secret diplomatic communication revealed Germany's proposal to Mexico, suggesting a military alliance in the event that the United States entered the war. Several key factors contributed to the outrage and disappointment felt by the American public and government officials alike.
Firstly, the content of the telegram was highly provocative. It disclosed Germany's intention to support Mexico in regaining territories lost in the Mexican-American War, particularly Texas, New Mexico, and Arizona. This territorial promise was seen as a direct threat to U.S. sovereignty.
Secondly, the telegram exemplified a violation of diplomatic etiquette and trust. The act of covertly soliciting an alliance with another country while secretly waging war against the United States was perceived as duplicitous and hostile.
Furthermore, the timing of the telegram’s interception was crucial. At a time when the U.S. was maintaining a policy of neutrality, the revelation provoked feelings of betrayal and indignation, particularly as many Americans were already leaning toward supporting the Allies. The following list summarizes the primary reasons for the upset:
- Threat to National Security: Proposal for military alliance with Mexico.
- Violation of Diplomacy: Espionage-like tactics undermining trust.
- Provocation of American Public Sentiment: Escalation of anti-German sentiment.
In conclusion, the Zimmermann Telegram served as a catalyst for change, propelling the United States from a stance of neutrality into active participation in World War I, underscoring the significance of transparent diplomatic communications.
Related Tags