Nicholas Novikov was a pivotal figure in Russian history, renowned for his contributions as both a journalist and a statesman. He was born in 1744 in St. Petersburg, a city that was then experiencing the heights of cultural and political fervor. From a young age, Novikov showed a deep interest in literature and the arts, which would later shape his career. His educational journey took him to the esteemed Serapion Brothers, a group of intellectuals who gathered to cultivate the arts and literature.
Novikov's life was a tapestry woven with various threads of influence—from the Enlightenment ideals bubbling across Europe to the sociopolitical challenges of his homeland. He actively engaged with the Russian Enlightenment, advocating for reforms in society and governance. After gaining recognition for his writings, he founded the first Russian magazine, “Yaichnaya Dozhdi”, which focused on raising public awareness about educational and political issues.
Despite his accomplishments, Novikov faced considerable challenges, particularly from the authorities. His progressive ideas often put him at odds with the ruling class, leading to a series of incarcerations that highlighted the tension between creative expression and state control in Russia. Throughout his life, he continued to champion freedom of thought, making significant contributions to public discourse.
In summary, Nicholas Novikov's life was characterized by a relentless pursuit of knowledge and social improvement, making him an essential voice in the landscape of Russian literature and politics during his time.
When Did Novikov Write His Telegram?
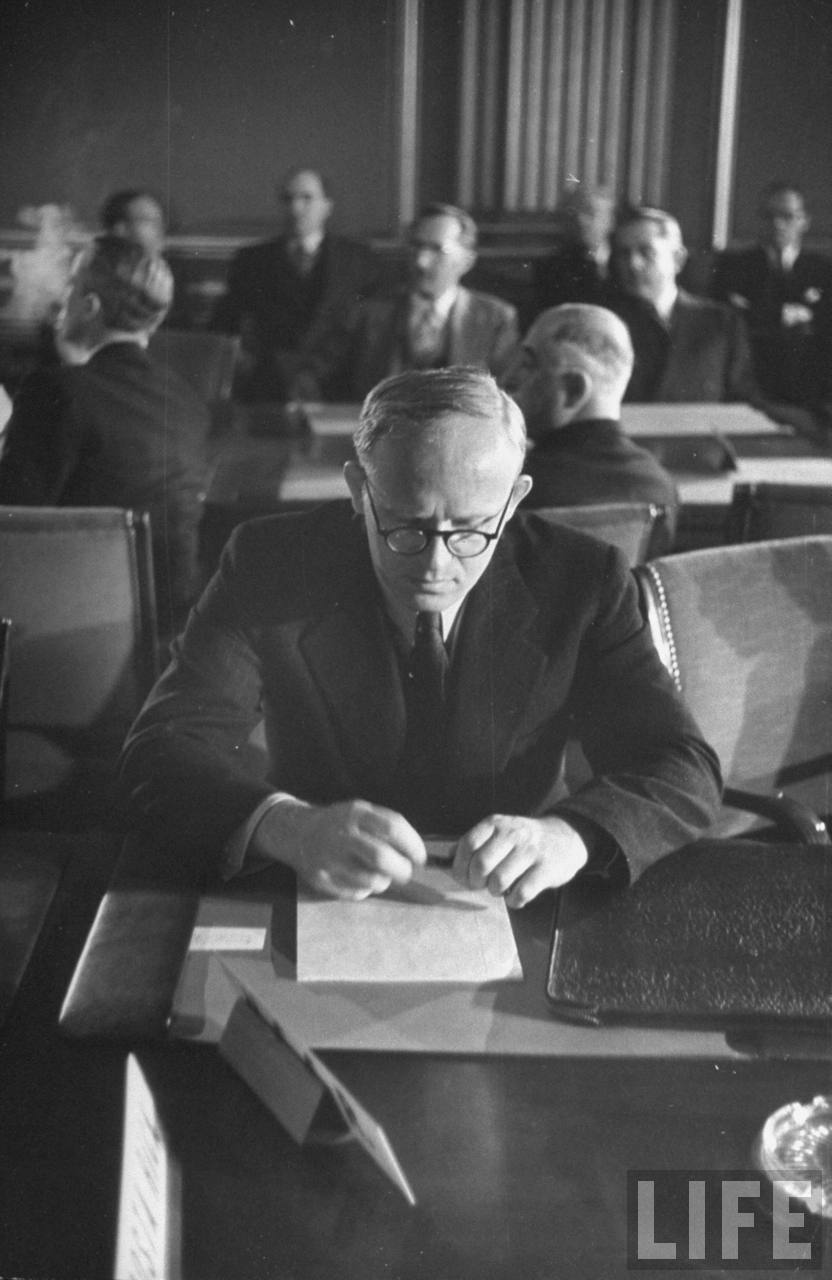

The telegram that Nicholas Novikov is most famous for was penned in the year 1793. This was a pivotal period, not just for Novikov, but for Russia as a whole. The backdrop of this telegram was the heightened political climate following the French Revolution, which sent shockwaves through Europe and reached even the conservative corridors of power in Russia.
Novikov's telegram was a call to action, addressing key figures in the Russian government about the need for reforms. This moment in time was marked by a series of events that compelled intellectuals like Novikov to challenge the status quo. He aimed to shed light on the injustices and desires for change that permeated society, urging leaders to take heed of the shifting tides.
What's fascinating is that the telegram wasn’t just a one-off communication; it was a culmination of his thoughts and observations gathered over years of advocating for reform. The urgency in his writing reflected the mounting tension in a Russia caught between tradition and the ideals of progress.
Ultimately, the year 1793 stands as a significant mark in Novikov’s legacy, showcasing his unwavering commitment to social change at a time when many were still fearful of repercussions. He anticipated that his words would resonate and spark meaningful dialogue around the need for reform, a true testament to his role as a thinker and activist of his era.
Who Was Nicholas Novikov and When Did He Write His Telegram?
Nicholas Novikov (1744-1818) was a prominent Russian public figure, writer, and influential intellectual during the reign of Catherine the Great. Born into a noble family, he became a significant advocate for the ideas of the Enlightenment, emphasizing reason, science, and education. Novikov was not just a writer; he was also a publisher who founded several magazines and dedicated himself to promoting literacy and knowledge among the Russian populace.
Novikov is best known for his literary works that critiqued the social and political landscape of Russia in the 18th century. His writings often touched on themes of freedom, Enlightenment philosophy, and social reform, paving the way for future Russian intellectual movements.
One of his notable contributions was the publication of a telegram addressing issues of censorship and the need for enlightenment in Russia. This telegram was written in 1790 during a time when Novikov faced repression due to his progressive ideas. The exact date of the telegram's writing can be placed in the late 1780s to early 1790s, capturing the essence of the struggles faced by thinkers of that era.
Key Contributions
- Enlightenment Advocate: Promoted ideas that shaped modern Russian thought.
- Publisher and Educator: Launched several periodicals that fostered a culture of reading.
- Social Critique: Addressed issues of censorship and societal reform in his works.
Table of Novikov's Major Works
| Year | Title | Focus |
|---|---|---|
| 1783 | Journal of the Russian Gentry | Social Issues |
| 1790 | Telegram on Censorship | Freedom of Speech |
Nicholas Novikov's legacy endures through the intellectual groundwork he laid for future generations. His advocacy for reform and promotion of Enlightenment ideals in Russia marked him as a pivotal figure in the history of Russian literature and social thought.
Related Tags