MariaDB is an open-source relational database management system that serves as a popular alternative to MySQL. It is designed for speed, scalability, and flexibility. Amazon Linux is a Linux server designed specifically for use in Amazon Web Services (AWS) environments, providing a stable, secure, and high-performance platform. Installing MariaDB on Amazon Linux allows users to leverage the ease of use and seamless integration of AWS while benefiting from the robust features of MariaDB. This guide will walk you through the steps necessary to install and configure MariaDB in Amazon Linux 2023.
System Requirements for Installing MariaDB
Before you install MariaDB on Amazon Linux, ensure that your system meets the following requirements:
- Operating System: Amazon Linux 2023
- RAM: At least 1 GB; more may be required for larger databases
- Disk Space: Minimum of 2 GB available for installation, with additional space based on data storage needs
- Processor: A compatible x86 or ARM-based architecture for Amazon EC2
- Network Connectivity: Internet access to download packages and updates
Ensure that you have administrative access to your Amazon Linux instance, as you will need to run commands with root privileges or use sudo to complete the installation process.
Additionally, it's important to keep your system updated. Running the latest version of Amazon Linux ensures compatibility and access to the latest security features. You should also configure security groups and firewall rules appropriately to allow traffic on the necessary ports for MariaDB, typically TCP port 3306.
Read This: How to Use an Amex Gift Card on Amazon
3. Step-by-Step Guide to Installing MariaDB

If you're ready to set up MariaDB on your Amazon Linux 2023 system, you're in the right place! This step-by-step guide will walk you through the installation process smoothly. Let's get started!
- Update your System: It's always a good practice to ensure your system is up-to-date before making any installations. Run the following command:
- Install MariaDB: Since MariaDB is available in the default Amazon Linux repositories, installing it is straightforward. Execute this command:
- Start the MariaDB Service: Once the installation is complete, you need to start the MariaDB service. Use the following command:
- Run the Secure Installation Script: MariaDB comes with a built-in script to help you secure your installation. Execute:
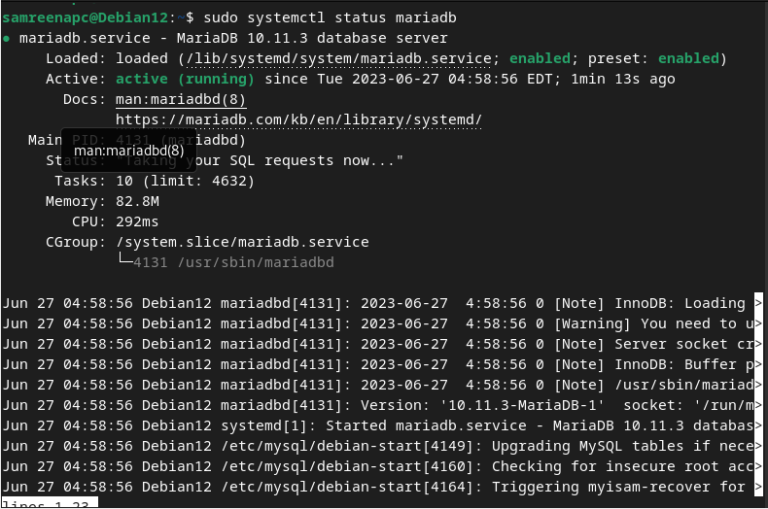
- Verify Installation: Finally, verify that MariaDB is running correctly by checking its status:
sudo yum update -y
sudo yum install mariadb-server -y
This command will fetch and install the MariaDB server along with necessary dependencies.
sudo systemctl start mariadb
To ensure that MariaDB starts on boot, run:
sudo systemctl enable mariadb
sudo mysql_secure_installation
This script will prompt you to set the root password, remove anonymous users, disallow remote root login, and remove test databases. Follow these prompts carefully!
sudo systemctl status mariadb
You should see an output indicating that the service is active and running.
That’s it! You now have MariaDB installed on your Amazon Linux 2023 instance. Let's move on to configuring it for your needs.
Read This: How to Self Publish on Amazon and Succeed
4. Configuring MariaDB after Installation
Congratulations on installing MariaDB! Now, let’s configure it to ensure optimal performance and security tailored to your use case. Here are some essential configuration steps:
- Accessing MariaDB: To start working with your MariaDB server, you’ll want to log in as the root user. Run:
- Creating a New Database: Once logged in, you can create a new database with:
- Creating a New User: It's a good idea to create a non-root user for daily operations. Here’s how to create a user:
- Granting Privileges: You’ll want to give your new user permissions to the new database. Use this command:
- Adjusting Configuration Files: For advanced users, you may want to edit the MariaDB configuration file located at:
mysql -u root -p
Enter the password you set during the secure installation process.
CREATE DATABASE mydatabase;
CREATE USER 'newuser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'password';
Don't forget to replace 'newuser' and 'password' with your desired username and a strong password.
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON mydatabase. TO 'newuser'@'localhost';
Remember to run:
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
to apply the changes.
/etc/my.cnf
Here, you can adjust parameters like buffer sizes to optimize performance based on your specific application needs.
By following these steps, you’ll have a securely configured MariaDB server ready to handle your database needs. Happy developing!
Read This: How to Effectively Contact a Seller on Amazon
5. Securing Your MariaDB Installation
Securing your MariaDB installation is crucial to protect your data and keep your database environment safe from potential threats. Here are some essential steps you can take to secure your MariaDB installation on Amazon Linux.
- Run the Security Script: After installing MariaDB, start by running the
mysql_secure_installationscript. This script will prompt you to set a root password, remove anonymous users, restrict root access to the local machine, and delete the test database. Simply follow the on-screen prompts to enhance security. - Change the Default Port: By default, MariaDB listens on port 3306. Changing this port can help obscure your database from automated attacks. To change the port:
- Open the configuration file with
sudo vi /etc/my.cnf. - Add or modify the line:
port = NEW_PORT_NUMBER.
- Open the configuration file with
- Restrict Host Access: Limit the IP addresses that can connect to your MariaDB server. You can do this by setting up firewall rules or configuring MariaDB user privileges with specific host access.
- Use Strong Passwords: Ensure that all database user passwords are strong, containing a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Avoid using easily guessable passwords.
Additionally, regularly update MariaDB and your operating system to keep vulnerabilities at bay. Remember, security is an ongoing process, so make sure to audit regular access logs and user accounts to maintain a tight ship!
Read This: How to Speak to a Live Person at Amazon
6. How to Manage MariaDB on Amazon Linux
Managing MariaDB on Amazon Linux can be done effectively with a few commands and tools. Here’s a quick guide on how to get started and what commands you’ll need to know.
First, you’ll want to familiarize yourself with some basic MariaDB commands. Here’s a simple cheat sheet:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
sudo systemctl start mariadb |
Start the MariaDB service. |
sudo systemctl stop mariadb |
Stop the MariaDB service. |
sudo systemctl restart mariadb |
Restart the MariaDB service. |
sudo systemctl status mariadb |
Check the status of the MariaDB service. |
mysql -u root -p |
Log in to the MariaDB server as the root user. |
In addition to these commands, consider using the MariaDB client, which provides a command-line interface to interact with your databases. You can perform various operations like creating databases, managing users, and executing queries directly from the terminal.
Moreover, for more advanced management, you can set up monitoring tools like MariaDB Monitor or integrate with AWS services such as CloudWatch for better visibility into your database performance.
Whether you’re running a small website or a large application, managing MariaDB efficiently ensures a smooth and reliable database experience.
Read This: How to Search Effectively on Amazon
Troubleshooting Common Installation Issues
While installing MariaDB on Amazon Linux can be straightforward, you might run into a few hiccups along the way. Don't worry—most installation issues are easily resolved with a bit of troubleshooting. Here are some common problems and their solutions:
- Dependency Errors: If you encounter errors about missing dependencies, try running
sudo yum updateto ensure that your package manager is up-to-date. This will help avoid conflicts and missing packages. - Firewall Issues: If you can't connect to your MariaDB server after installation, it could be a firewall issue. Use the following commands to allow traffic through the necessary port (default is 3306):
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=3306/tcp --permanent sudo firewall-cmd --reload
- Authentication Problems: If you're having trouble logging in, remember that MariaDB uses the `root` user by default. If you’ve set a password, double-check it. If you've forgotten it, you might need to reset the root password.
- Service Not Starting: If the MariaDB service won't start, check for errors in the log file located at
/var/log/mariadb/mariadb.log. Usesudo systemctl status mariadbfor additional insights on what might be going wrong. - Version Conflicts: If you've previously attempted to install different versions of MariaDB, clean up your system by removing old installations with
sudo yum remove mariadbbefore reinstallation.
Remember, the community forums and documentation can be invaluable resources if you're still encountering issues. Don't hesitate to seek help from fellow users!
Read This: Ultimate Guide to Navigating Amazon Prime
Best Practices for Using MariaDB on Amazon Linux
Once you've successfully installed MariaDB on Amazon Linux, it's essential to follow some best practices to ensure optimal performance and security. Here are several tips to help you get the most out of your MariaDB installation:
- Regular Backups: Always take regular backups of your databases. You can use the
mysqldumptool to create backups easily:mysqldump -u root -p --all-databases > all_databases_backup.sql
- Optimize Configuration: Tinker with your
my.cnfconfiguration file. Adjust settings like buffer pool size and connection limits based on your application’s workload for better performance. - Secure Your Installation: Run
mysql_secure_installationto enhance your MariaDB security. This utility will guide you in removing anonymous users, disallowing root access remotely, and more. - Monitor Performance: Use monitoring tools such as Percona Toolkit or Grafana for insights about your database's performance and to identify slow queries that can be optimized.
- Regular Updates: Keep MariaDB up to date to benefit from performance enhancements and security fixes by scheduling periodic checks for updates:
sudo yum update mariadb
By following these best practices, you can ensure that your MariaDB instance remains robust, secure, and performant, ready to handle your application's demands.
```html
Read This: How to Delete an Address from Amazon
How to Install MariaDB in Amazon Linux 2023
Installing MariaDB on Amazon Linux 2023 can be a straightforward process if you follow the right steps. MariaDB is a popular open-source database system and a great alternative to MySQL. Here’s a complete guide to help you set it up seamlessly on your Amazon Linux 2023 instance.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure you have the following:
- An Amazon Linux 2023 instance running.
- Root or sudo access to the instance.
- Updated package repositories.
Step-by-Step Installation
Follow these steps to install MariaDB:
- *Update Your System
- Install MariaDB
- Start the MariaDB Service
- Enable MariaDB to Start on Boot
- Secure the Installation*
Start by updating your system's packages to ensure you have the latest versions:
sudo dnf update -y
Now, you can install MariaDB using the following command:
sudo dnf install mariadb-server -y
Once installed, you need to start the MariaDB service:
sudo systemctl start mariadb
To ensure that MariaDB starts automatically on boot, enable the service:
sudo systemctl enable mariadb
After starting the service, run the security script to secure your installation:
sudo mysql_secure_installation
This script will prompt you to set the root password, remove anonymous users, and other security measures.
Verifying the Installation
To verify that MariaDB is installed correctly, log in to the MariaDB console:
mysql -u root -p
If you can access the console, your installation was successful!
Conclusion
Installing MariaDB on Amazon Linux 2023 is a straightforward process involving system updates, package installation, and service configuration. With MariaDB set up, you're ready to begin creating your databases and applications efficiently!
Additional Resources
For further reading and advanced configurations, consider these resources:
```
Related Tags